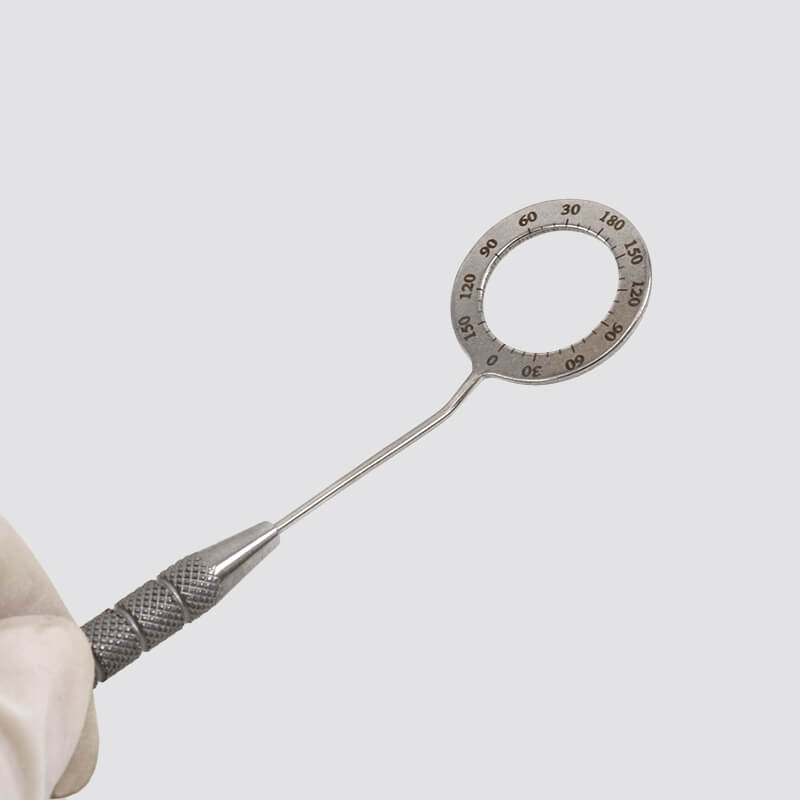
What are some essential surgical instruments for different procedures?
Surgical instruments are vital tools used during various medical procedures to perform precise and delicate tasks. These instruments help surgeons achieve better accuracy, reduce trauma to surrounding tissues, and improve patient outcomes.
The development of advanced surgical instruments has revolutionized the field of medicine by enabling surgeons to perform complex surgeries with minimal invasiveness.
There is a wide range of surgical instruments designed for specific procedures and purposes. Here are some essential surgical instruments that are commonly used in different types of surgeries:
- Scalpel: A scalpel is a small, sharp knife used for making incisions or cuts on the skin or other tissues. It comes in different blade sizes and shapes, including straight, curved, and serrated edges, depending on the type of incision required.
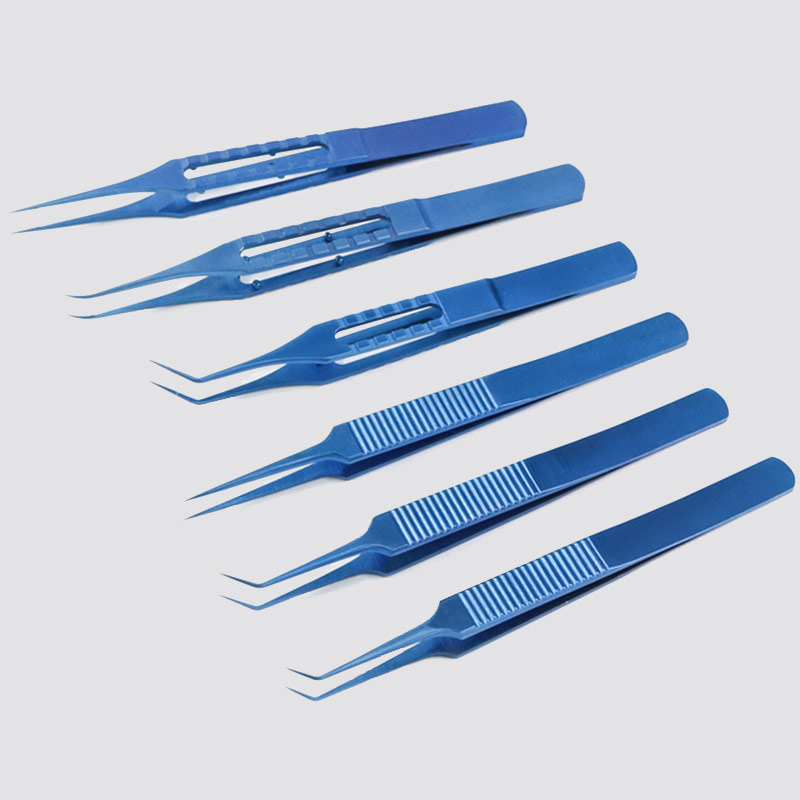
- Forceps: Forceps are used to hold and manipulate tissues during surgery. They have two blades that can be locked together to grasp objects firmly without causing any damage.
- Retractors: Retractors are specialized surgical instruments used to keep an incision open or move organs aside during surgery. They come in various sizes and shapes, such as self-retaining retractors that hold themselves in place without needing assistance from a surgeon.
- Scissors: Surgical scissors come in various designs suited for different purposes like cutting sutures or trimming tissues during surgery.
- Hemostatic clamps: These clamps are designed to control bleeding by compressing blood vessels temporarily until they can be ligated or cauterized.
- Trocars: Trocars are thin hollow tubes with sharp tips used to create access points for inserting laparoscopic instruments into the body cavity for minimally invasive surgeries.
- Suction devices: Suction devices use negative pressure to remove fluids or debris from the surgical site, ensuring clear visibility for the surgeon.
- Needles and sutures: Needles attached to suture materials like silk thread or monofilament are used to close surgical incisions and repair tissue damage.
- Forceps-sealing devices: These instruments combine the functions of a forceps and a sealing device, allowing surgeons to grasp tissues and seal them simultaneously with minimal trauma.
In addition to these essential surgical instruments, there are many more specialized tools used for specific procedures like endoscopy, microsurgery, orthopedics, etc. As technology advances, newer and more efficient instruments are being developed to aid in surgeries, making them safer and less invasive for patients. It is crucial for surgeons to have a thorough understanding of these instruments’ features and applications to choose the right one for each procedure.
Do surgical instruments require special maintenance?

Cleaning, disinfection, sterilization, and distribution of surgical instruments are all completed by the supply room, and this blog shares with you the content of the maintenance and repair of surgical instruments.
Routine maintenance of surgical instruments
Pre-treatment before cleaning
After the operation, first soak the surgical instruments with multi-enzyme cleaning agent for 5-10min, so that the dirt remaining on the surface of the surgical instruments and in the suture of the mechanical connection parts can be decomposed and softened, do not soak them directly in hot water, alcohol, disinfectant or antiseptic, which will make the mucus, blood or other body fluids coagulate, and affect the next step of the cleaning. For complex and difficult-to-handle parts, you can first disassemble the surgical instrument, disassemble, and keep each part for assembly after treatment.
Cleaning

Articulated surgical instruments should be opened when cleaning, microsurgical instruments, plated surgical instruments and fine surgical instruments should be cleaned manually to avoid the bumping of the tip of fine microsurgical instruments. After cleaning, put them in the oven at about 50℃ or room temperature to dry, avoiding contact with moisture or liquid for a long time, after drying, put them in the surgical instrument box or pack them with a special cotton cloth in an orderly manner according to the types of surgical instruments.
Rust Removal
If the surgical instruments have been left unused for a long time and become rusty, rust remover can be sprayed on the rusted parts and then brushed with soft bristles for manual rust removal. Similarly, during the brushing process, the various joints of the surgical instruments should be opened and fully brushed.
Lubrication/Assembly
The surgical instruments are lubricated with lubricant every time they are used and processed, and the surgical instruments are kept dry before lubrication, and after lubrication, the surgical instruments are disassembled and reassembled and inspected to avoid damage, cracks, misalignment and corrosion, and at the same time, the working parts should be mechanically inspected to make sure that each piece of the surgical instruments is functioning well.
Storage

These precautions help to ensure that surgical instruments are clean, effective, and in long-term use. If you want to know more about surgical instruments and operating room equipment-related information, you can continue to pay attention to the Surgical-tool.

 Capsulorhexis Forceps
Capsulorhexis Forceps Suture Forceps
Suture Forceps Hemostatic Forceps
Hemostatic Forceps Chalazion Forceps
Chalazion Forceps Adson Forceps
Adson Forceps Tissue Forceps
Tissue Forceps